What Exactly is Regenerative Medicine? A Short Guide
December 14, 2021
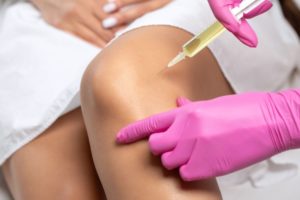
Right now, the fastest-growing field in all of healthcare is regenerative medicine, with clinics popping up across the world and doctors filling up training courses year-round. However, it’s something that the average person hasn’t heard of, even though literally millions of people benefit from it each year. What exactly is regenerative medicine, and what kinds of problems can it treat? To get answers to these questions and more, be sure to read the short guide below.
The Basics of Regenerative Medicine
The goal of regenerative medicine is to focus and stimulate the body’s natural healing response in order to treat a wide variety of musculoskeletal conditions. Rather than fixing the problem invasively (like with surgery) or just reducing the symptoms (like medication), regenerative medicine is designed to address the underlying source of a problem in the most gentle, natural, and direct way possible. This is primarily done by applying treatments designed to work with the body’s ability to repair itself.
What Can Regenerative Medicine Treat?
The scope of regenerative medicine is vast, and it has been used to help patients dealing with the following issues (and many more):
- Osteoarthritis
- Headaches/Migraines
- Various Sprains and Strains
- Peri-Natal Pain
- Tendinitis
- Carpal Tunnel and Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Tennis/Golfer’s Elbow
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Labrum Tear
- Rotator Cuff Injury
- Back Pain
- Neck Pain
- Knee Pain
- Nerve Entrapment
- Aging Skin
- Thinning Hair
Common Regenerative Treatments
A few of the most popular regenerative medicine treatments include:
- Prolotherapy: A combination of dextrose (sugar) and lidocaine is injected into an injured area of the body. The lidocaine numbs the patient, and the sugar irritates the affected tissues without harming them. This triggers a repair response from the body and “tricks” it into focusing it right on the injury.
- PRP: Platelet-rich plasma is a substance derived from a small sample of a patient’s blood that encourages accelerated healing, pain reduction, and improved function. It contains a much higher concentration of platelets and growth factors/proteins than regular blood.
- Amniotic Growth Factors: Cells derived from amniotic fluid are injected into the injured area, which helps the tissues repair themselves relatively quickly while experiencing much less pain and stiffness.
This is just scratching the surface when it comes to regenerative medicine, and new findings are discovered each year thanks to robust research being conducted around the globe. If you’re dealing with a chronic or acute injury, and you want a treatment that doesn’t involve strong medication or expensive surgery, regenerative medicine might be the holistic solution you’ve been searching for.
About the Author
Dr. Joel Stein has almost 40 years of experience as an osteopathic physician, and he trained at the prestigious Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine, now known as Andrew Taylor Still University. Over the years, he has earned a reputation for being able to fix problems that other doctors cannot, and he’s proud to carry on his father’s tradition of offering personalized, effective healthcare for all types of people. To learn more about regenerative medicine or schedule an appointment at the Institute for Non-Surgical Orthopedics, click here.
No Comments
No comments yet.
RSS feed for comments on this post.
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.